Abstract
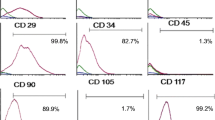
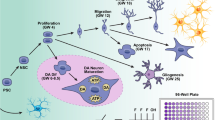
Differentiating neuronal cells derived from human umbilical cord blood stem cells have been used as an in vitro tool for the assessment of developmental neurotoxicity of monocrotophos (MCP), an organophosphate pesticide. The differentiating cells were exposed to MCP during the different stages of maturation, viz., days 2, 4, and 8, and changes in the makers of cell proliferation, neuronal differentiation, neuronal injuries, and receptors were studied. We found significant upregulation in the different MAPKs, apoptosis, and neurogenesis markers and downregulation in the cell proliferation markers during neuronal differentiation. We further identified significant upregulation in the expression of different MAPKs and proteins involved in oxidative stress, apoptosis, and calpain pathways in the mid-differentiating cells exposed to MCP. The upregulated levels of these proteins seem to be the main cause of alteration during the differentiation process towards apoptosis as a fine-tune of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins are desirable for the process of differentiation without apoptosis. The decreased acetylcholinesterase activity, dopaminergic, and cholinergic receptors and increased acetylcholine levels in the differentiating neuronal cells indicate the vulnerability of these cells towards MCP-induced neurotoxicity. Our data confirms that differentiating neuronal cells derived from human umbilical cord stem cells could be used as a powerful tool to assess the developmental neurotoxicity in human beings.









Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
01 July 2019
The original version of this article unfortunately contained a mistake. The acknowledgment published was incomplete.
01 July 2019
The original version of this article unfortunately contained a mistake. The acknowledgment published was incomplete.
References
Goldman LR, Koduru S (2000) Chemicals in the environment and developmental toxicity to children: a public health and policy perspective. Environ Health Perspect 108(Suppl 3):443–448
Roberts EM, English PB, Grether JK, Windham GC, Somberg L, Wolff C (2007) Maternal residence near agricultural pesticide applications and autism spectrum disorders among children in the California Central Valley. Environ Health Perspect 115:1482–1489
Bradman A, Barr DB, Claus Henn BG, Drumheller T, Curry C, Eskenazi B (2003) Measurement of pesticides and other toxicants in amniotic fluid as a potential biomarker of prenatal exposure: a validation study. Environ Health Perspect 111:1779–1782
Whyatt RM, Camann D, Perera FP, Rauh VA, Tang D, Kinney PL, Garfinkel R, Andrews H, Hoepner L, Barr DB (2005) Biomarkers in assessing residential insecticide exposures during pregnancy and effects on fetal growth. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 206:246–254
Berkowitz GS, Wetmur JG, Birman-Deych E, Obel J, Lapinski RH, Godbold JH, Holzman IR, Wolff MS (2004) In utero pesticide exposure, maternal paraoxonase activity, and head circumference. Environ Health Perspect 112:388–391
Whyatt RM, Rauh V, Barr DB, Camann DE, Andrews HF, Garfinkel R, Hoepner LA, Diaz D, Dietrich J, Reyes A, Tang D, Kinney PL, Perera FP (2004) Prenatal insecticide exposures and birth weight and length among an urban minority cohort. Environ Health Perspect 112:1125–1132
Young JG, Eskenazi B, Gladstone EA, Bradman A, Pedersen L, Johnson C, Barr DB, Furlong CE, Holland NT (2005) Association between in utero organophosphate pesticide exposure and abnormal reflexes in neonates. Neurotoxicology 26:199–209
Engel SM, Berkowitz GS, Barr DB, Teitelbaum SL, Siskind J, Meisel SJ, Wetmur JG, Wolff MS (2007) Prenatal organophosphate metabolite and organochlorine levels and performance on the Brazelton Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale in a multiethnic pregnancy cohort. Am J Epidemiol 165:1397–1404
Bouchard MF, Chevrier J, Harley KG, Kogut K, Vedar M, Calderon N, Trujillo C, Johnson C, Bradman A, Barr DB, Eskenazi B (2011) Prenatal exposure to organophosphate pesticides and IQ in 7-year-old children. Environ Health Perspect 119:1189–1195
Engel SM, Wetmur J, Chen J, Zhu C, Barr DB, Canfield RL, Wolff MS (2011) Prenatal exposure to organophosphates, paraoxonase 1, and cognitive development in childhood. Environ Health Perspect 119:1182–1188
Rauh V, Arunajadai S, Horton M, Perera F, Hoepner L, Barr DB, Whyatt R (2011) Seven-year neurodevelopmental scores and prenatal exposure to chlorpyrifos, a common agricultural pesticide. Environ Health Perspect 119:1196–1201
Kashyap MP, Singh AK, Kumar V, Tripathi VK, Srivastava RK, Agrawal M, Khanna VK, Yadav S, Jain SK, Pant AB (2011) Monocrotophos induced apoptosis in PC12 cells: role of xenobiotic metabolizing cytochrome P450s. PLoS ONE 6:e17757
Kashyap MP, Singh AK, Kumar V, Yadav DK, Khan F, Jahan S, Khanna VK, Yadav S, Pant AB (2013) Pkb/Akt1 mediates Wnt/GSK3beta/beta-catenin signaling-induced apoptosis in human cord blood stem cells exposed to organophosphate pesticide monocrotophos. Stem Cells Dev 22(2):224–238
Kashyap MP, Singh AK, Siddiqui MA, Kumar V, Tripathi VK, Khanna VK, Yadav S, Jain SK, Pant AB (2010) Caspase cascade regulated mitochondria mediated apoptosis in monocrotophos exposed PC12 cells. Chem Res Toxicol 23:1663–1672
Singh AK, Kashyap MP, Jahan S, Kumar V, Tripathi VK, Siddiqui MA, Yadav S, Khanna VK, Das V, Jain SK, Pant AB (2012) Expression and inducibility of cytochrome P450s (CYP1A1, 2B6, 2E1, 3A4) in human cord blood CD34+ stem cell-derived differentiating neuronal cells. Toxicol Sci 129:392–410
Rauh VA, Perera FP, Horton MK, Whyatt RM, Bansal R, Hao X, Liu J, Barr DB, Slotkin TA, Peterson BS (2012) Brain anomalies in children exposed prenatally to a common organophosphate pesticide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:7871–7876
Lein P, Locke P, Goldberg A (2007) Meeting report: alternatives for developmental neurotoxicity testing. Environ Health Perspect 115:764–768
Eddleston M, Buckley NA, Eyer P, Dawson AH (2008) Management of acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning. Lancet 371:597–607
Slotkin TA, Seidler FJ (2011) Developmental exposure to organophosphates triggers transcriptional changes in genes associated with Parkinson's disease in vitro and in vivo. Brain Res Bull 86:340–347
Slotkin TA, Seidler FJ (2012) Developmental neurotoxicity of organophosphates targets cell cycle and apoptosis, revealed by transcriptional profiles in vivo and in vitro. Neurotoxicol Teratol 34:232–241
Grandjean P, Landrigan PJ (2006) Developmental neurotoxicity of industrial chemicals. Lancet 368:2167–2178
Lein P, Silbergeld E, Locke P, Goldberg AM (2005) In vitro and other alternative approaches to developmental neurotoxicity testing (DNT). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 19:735–744
Resnik DB, Portier C (2005) Pesticide testing on human subjects: weighing benefits and risks. Environ Health Perspect 113:813–817
Slotkin TA, Card J, Seidler FJ (2012) Chlorpyrifos developmental neurotoxicity: interaction with glucocorticoids in PC12 cells. Neurotoxicol Teratol 34:505–512
Dishaw LV, Powers CM, Ryde IT, Roberts SC, Seidler FJ, Slotkin TA, Stapleton HM (2011) Is the PentaBDE replacement, tris (1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TDCPP), a developmental neurotoxicant? Studies in PC12 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 256:281–289
de Groot MW, Westerink RH, Dingemans MM (2012) Don't judge a neuron only by its cover: neuronal function in in vitro developmental neurotoxicity testing. Toxicol Sci 132(1):1–7
Visan A, Hayess K, Sittner D, Pohl EE, Riebeling C, Slawik B, Gulich K, Oelgeschlager M, Luch A, Seiler AE (2012) Neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells as a tool to assess developmental neurotoxicity in vitro. Neurotoxicology 33:1135–1146
Fritsche E, Gassmann K, Schreiber T (2011) Neurospheres as a model for developmental neurotoxicity testing. Methods Mol Biol 758:99–114
Siddiqui MA, Singh G, Kashyap MP, Khanna VK, Yadav S, Chandra D, Pant AB (2008) Influence of cytotoxic doses of 4-hydroxynonenal on selected neurotransmitter receptors in PC-12 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 22:1681–1688
Gluckman E (2011) Milestones in umbilical cord blood transplantation. Blood Rev 25:255–259
Zanier ER, Montinaro M, Vigano M, Villa P, Fumagalli S, Pischiutta F, Longhi L, Leoni ML, Rebulla P, Stocchetti N, Lazzari L, De Simoni MG (2011) Human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells protect mice brain after trauma. Crit Care Med 39:2501–2510
Larosa F, Deconinck E, Helias P, Fontan J, Heczko M, Brion A, Ledu K, Delaby P, Vuiller J, Ferrand C, Saas P, Pouthier F, Dormoy A, Chabod J, Malugani C, Rohrlich PS, Legrand F (2011) Successful mobilization and engraftment of PBSCs derived from donor cord blood cells after a previous allogeneic RIC single unrelated cord blood transplantation. Blood 118:476–478
Moore MA (1991) Review: Stratton Lecture 1990. Clinical implications of positive and negative hematopoietic stem cell regulators. Blood 78:1–19
Ogawa M (1993) Differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 81:2844–2853
Metcalf D (1993) Hematopoietic regulators: redundancy or subtlety? Blood 82:3515–3523
Lyman SD (1995) Biology of flt3 ligand and receptor. Int J Hematol 62:63–73
Borge OJ, Ramsfjell V, Cui L, Jacobsen SE (1997) Ability of early acting cytokines to directly promote survival and suppress apoptosis of human primitive CD34 + CD38− bone marrow cells with multilineage potential at the single-cell level: key role of thrombopoietin. Blood 90:2282–2292
Tsukahara S, Ikeda R, Goto S, Yoshida K, Mitsumori R, Sakamoto Y, Tajima A, Yokoyama T, Toh S, Furukawa K, Inoue I (2006) Tumour necrosis factor alpha-stimulated gene-6 inhibits osteoblastic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells induced by osteogenic differentiation medium and BMP-2. Biochem J 398:595–603
Zheng Y, Sun A, Han ZC (2005) Stem cell factor improves SCID-repopulating activity of human umbilical cord blood-derived hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in xenotransplanted NOD/SCID mouse model. Bone Marrow Transplant 35:137–142
Taguchi A (2011) Cell-based therapy for patients with vascular dementia. Psychogeriatrics 11:113–115
Stellos K, Panagiota V, Sachsenmaier S, Trunk T, Straten G, Leyhe T, Seizer P, Geisler T, Gawaz M, Laske C (2010) Increased circulating progenitor cells in Alzheimer's disease patients with moderate to severe dementia: evidence for vascular repair and tissue regeneration? J Alzheimers Dis 19:591–600
Huang EJ, Reichardt LF (2001) Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:677–736
Woo CW, Lucarelli E, Thiele CJ (2004) NGF activation of TrkA decreases N-myc expression via MAPK path leading to a decrease in neuroblastoma cell number. Oncogene 23:1522–1530
Benito-Gutierrez E, Garcia-Fernandez J, Comella JX (2006) Origin and evolution of the Trk family of neurotrophic receptors. Mol Cell Neurosci 31:179–192
Sanchez-Ramos JR, Song S, Kamath SG, Zigova T, Willing A, Cardozo-Pelaez F, Stedeford T, Chopp M, Sanberg PR (2001) Expression of neural markers in human umbilical cord blood. Exp Neurol 171:109–115
Zigova T, Song S, Willing AE, Hudson JE, Newman MB, Saporta S, Sanchez-Ramos J, Sanberg PR (2002) Human umbilical cord blood cells express neural antigens after transplantation into the developing rat brain. Cell Transplant 11:265–274
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu BE, Karandikar M, Berman K, Cobb MH (2001) Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 22:153–183
Obara Y, Nakahata N (2010) The signaling pathway leading to extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) activation via G-proteins and ERK5-dependent neurotrophic effects. Mol Pharmacol 77:10–16
Besnard A, Galan-Rodriguez B, Vanhoutte P, Caboche J (2011) Elk-1 a transcription factor with multiple facets in the brain. Front Neurosci 5:35
Greenblatt MB, Shim JH, Zou W, Sitara D, Schweitzer M, Hu D, Lotinun S, Sano Y, Baron R, Park JM, Arthur S, Xie M, Schneider MD, Zhai B, Gygi S, Davis R, Glimcher LH (2010) The p38 MAPK pathway is essential for skeletogenesis and bone homeostasis in mice. J Clin Invest 120:2457–2473
Hamidouche Z, Fromigue O, Ringe J, Haupl T, Marie PJ (2010) Crosstalks between integrin alpha 5 and IGF2/IGFBP2 signalling trigger human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal osteogenic differentiation. BMC Cell Biol 11:44
Kiec-Wilk B, Grzybowska-Galuszka J, Polus A, Pryjma J, Knapp A, Kristiansen K (2010) The MAPK-dependent regulation of the Jagged/Notch gene expression by VEGF, bFGF or PPAR gamma mediated angiogenesis in HUVEC. J Physiol Pharmacol 61:217–225
Li Z, Theus MH, Wei L (2006) Role of ERK 1/2 signaling in neuronal differentiation of cultured embryonic stem cells. Dev Growth Differ 48:513–523
Gerety SS, Wilkinson DG (2011) Morpholino artifacts provide pitfalls and reveal a novel role for pro-apoptotic genes in hindbrain boundary development. Dev Biol 350:279–289
Fernando P, Brunette S, Megeney LA (2005) Neural stem cell differentiation is dependent upon endogenous caspase 3 activity. FASEB J 19:1671–1673
Sakamaki K, Inoue T, Asano M, Sudo K, Kazama H, Sakagami J, Sakata S, Ozaki M, Nakamura S, Toyokuni S, Osumi N, Iwakura Y, Yonehara S (2002) Ex vivo whole-embryo culture of caspase-8-deficient embryos normalize their aberrant phenotypes in the developing neural tube and heart. Cell Death Differ 9:1196–1206
Rebe C, Cathelin S, Launay S, Filomenko R, Prevotat L, L'Ollivier C, Gyan E, Micheau O, Grant S, Dubart-Kupperschmitt A, Fontenay M, Solary E (2007) Caspase-8 prevents sustained activation of NF-kappaB in monocytes undergoing macrophagic differentiation. Blood 109:1442–1450
Cullen SP, Martin SJ (2009) Caspase activation pathways: some recent progress. Cell Death Differ 16:935–938
Conacci-Sorrell M, Eisenman RN (2011) Post-translational control of Myc function during differentiation. Cell Cycle 10:604–610
Damon DH, Teriele JA, Marko SB (2007) Vascular-derived artemin: a determinant of vascular sympathetic innervation? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H266–H273
Jeong DG, Park WK, Park S (2008) Artemin activates axonal growth via SFK and ERK-dependent signalling pathways in mature dorsal root ganglia neurons. Cell Biochem Funct 26:210–220
Isoda H, Talorete TP, Han J, Oka S, Abe Y, Inamori Y (2005) Effects of organophosphorous pesticides used in china on various mammalian cells. Environ Sci 12:9–19
Das PP, Shaik AP, Jamil K (2007) Genotoxicity induced by pesticide mixtures: in-vitro studies on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Toxicol Ind Health 23:449–458
Jose S, Jayesh P, Mohandas A, Philip R, Bright Singh IS (2011) Application of primary haemocyte culture of Penaeus monodon in the assessment of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of heavy metals and pesticides. Mar Environ Res 71:169–177
Moser VC (2011) Age-related differences in acute neurotoxicity produced by mevinphos, monocrotophos, dicrotophos, and phosphamidon. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:451–457
Casale GP, Vennerstrom JL, Bavari S, Wang TL (1993) Inhibition of interleukin 2 driven proliferation of mouse CTLL2 cells, by selected carbamate and organophosphate insecticides and congeners of carbaryl. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 15:199–215
Kirby LA, Schott JT, Noble BL, Mendez DC, Caseley PS, Peterson SC, Routledge TJ, Patel NV (2012) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) inhibitor, SB-216763, promotes pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE 7:e39329
Doble BW, Patel S, Wood GA, Kockeritz LK, Woodgett JR (2007) Functional redundancy of GSK-3alpha and GSK-3beta in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling shown by using an allelic series of embryonic stem cell lines. Dev Cell 12:957–971
Kelly KF, Ng DY, Jayakumaran G, Wood GA, Koide H, Doble BW (2011) Beta-catenin enhances Oct-4 activity and reinforces pluripotency through a TCF-independent mechanism. Cell Stem Cell 8:214–227
Wray J, Kalkan T, Gomez-Lopez S, Eckardt D, Cook A, Kemler R, Smith A (2011) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 alleviates Tcf3 repression of the pluripotency network and increases embryonic stem cell resistance to differentiation. Nat Cell Biol 13:838–845
Niwa H, Ogawa K, Shimosato D, Adachi K (2009) A parallel circuit of LIF signalling pathways maintains pluripotency of mouse ES cells. Nature 460:118–122
Zimmer B, Schildknecht S, Kuegler PB, Tanavde V, Kadereit S, Leist M (2011) Sensitivity of dopaminergic neuron differentiation from stem cells to chronic low-dose methylmercury exposure. Toxicol Sci 121:357–367
Niquet J, Auvin S, Archie M, Seo DW, Allen S, Sankar R, Wasterlain CG (2007) Status epilepticus triggers caspase-3 activation and necrosis in the immature rat brain. Epilepsia 48:1203–1206
Lopez-Meraz ML, Wasterlain CG, Rocha LL, Allen S, Niquet J (2010) Vulnerability of postnatal hippocampal neurons to seizures varies regionally with their maturational stage. Neurobiol Dis 37:394–402
Carloni S, Carnevali A, Cimino M, Balduini W (2007) Extended role of necrotic cell death after hypoxia-ischemia-induced neurodegeneration in the neonatal rat. Neurobiol Dis 27:354–361
Kazi AI, Oommen A (2012) The effect of acute severe monocrotophos poisoning on inhibition, expression and activity of acetylcholinesterase in different rat brain regions. Neurotoxicology 33:1284–1290
Eskenazi B, Marks AR, Bradman A, Harley K, Barr DB, Johnson C, Morga N, Jewell NP (2007) Organophosphate pesticide exposure and neurodevelopment in young Mexican-American children. Environ Health Perspect 115:792–798
Rauh VA, Garfinkel R, Perera FP, Andrews HF, Hoepner L, Barr DB, Whitehead R, Tang D, Whyatt RW (2006) Impact of prenatal chlorpyrifos exposure on neurodevelopment in the first 3 years of life among inner-city children. Pediatrics 118:e1845–e1859
Bjorling-Poulsen M, Andersen HR, Grandjean P (2008) Potential developmental neurotoxicity of pesticides used in Europe. Environ Health 7:50
Brundin P, Kordower JH (2012) Neuropathology in transplants in Parkinson's disease: implications for disease pathogenesis and the future of cell therapy. Prog Brain Res 200:221–241
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to the Director, the IITR, Lucknow, India, for his keen interest to the study. The work was supported by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India, [Grant No. BSC0111/INDEPTH/CSIR Network Project] and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), New Delhi, India [Grant No. 102/IFD/SAN/PR-1524/2010-2011]. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the article.
Declaration of no conflict of interest
Authors of this manuscript have no conflict of interest among them or anybody else regarding the scientific contents, financial matters, or otherwise.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure S1
List of 96 genes studied using TaqMan low-density array (TLDA) in 384-well plate format (DOC 309 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kashyap, M.P., Kumar, V., Singh, A.K. et al. Differentiating neurons derived from human umbilical cord blood stem cells work as a test system for developmental neurotoxicity. Mol Neurobiol 51, 791–807 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8716-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8716-7